Categories
Recent Posts
A PCB is a board of non-conductive material, such as fibreglass or composite epoxy, with a layer of conductive copper traces etched onto its surface. These traces form circuits that allow electrical signals to flow between components.
An important aspect of printed circuit boards is the concept of layer count. Layer count refers to the number of conductive layers in a PCB, which determines its complexity and functionality. PCBs can range from single layer designs to multi-layer designs.
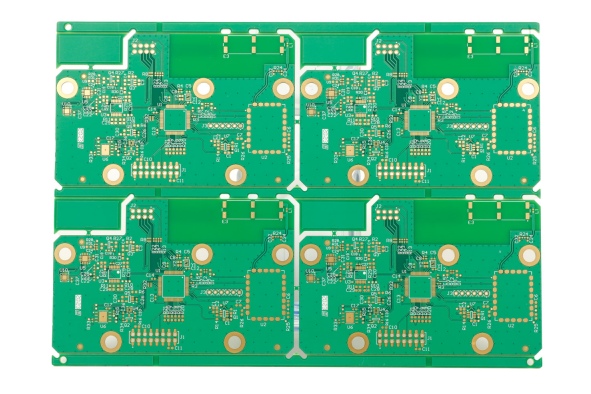
The number of layers directly affects a PCB's ability to handle complex circuitry, power distribution, signal integrity and overall performance. Higher layer counts allow for more complex and dense designs, enabling the inclusion of additional components and advanced functionality.
Understanding the concept of PCB layer count is critical for designers and engineers as it directly affects the capabilities and limitations of a given PCB design. By carefully selecting the appropriate number of layers, Ucreate's design department guides you through the process of optimising the performance, size and functionality of your electronic devices.
Understanding 4-Layer PCBs and Their Distinctions
1. What isa 4-Layer PCB?
A 4-layer PCB is a type of printed circuit board that consists of four layers of conductive material separated by layers of insulation. These four layers include two internal signal layers and two internal power or ground plane layers. The layers are interconnected by vias, which are conductive paths that allow signals and power to pass between layers.
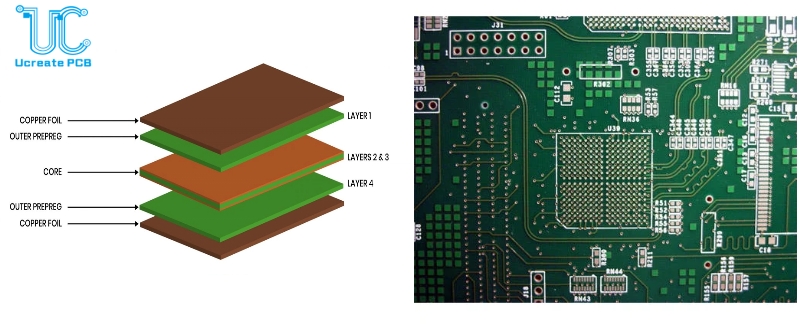
2.Comparison with Single and Double Layer PCBs
Single-layer PCBs have only one layer of conductive material, usually copper, on one side of the board. They are commonly used for simple and low-complexity circuits due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, they have limited routing options and are not suitable for complex designs.
Double sided PCBs offer increased routing flexibility and are suitable for moderately complex designs. They consist of two layers of conductive material connected through vias, allowing signal traces to be routed on both sides of the board. However, it is important to note that they may have limitations in terms of power distribution and signal integrity.
3. Key Difference
5 layer PCBs offer significantly greater design flexibility compared to single and double layer PCBs. The additional internal signal and plane layers provide more routing options, allowing for complex circuit designs, higher component density, and improved signal integrity.
4-layer PCBs feature internal power and ground plane layers that provide a solid reference for signal traces, effectively minimizing noise, crosstalk, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). This results in improved signal integrity and reduced susceptibility to external disturbances.
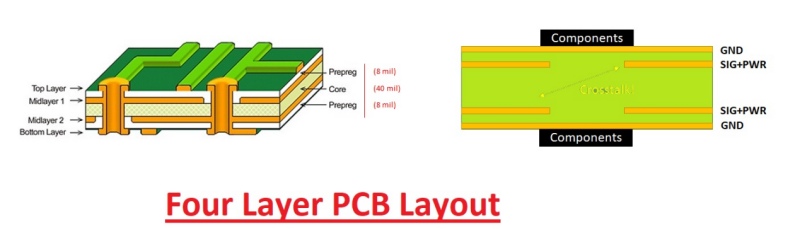
4-layer circuit board facilitate efficient power distribution through the presence of internal power and ground plane layers.
The power planes provide low impedance paths for power supply and ground connections, reducing voltage drops and ensuring stable and reliable power distribution throughout the board. Additionally, 4-layer PCBs allow for more compact designs compared to lower layer counts. The internal layers added to the design enable more compact component placement and trace routing, making them highly suitable for space-limited applications.
By taking advantage of 4-layer PCBs, Ucreate's design department can achieve greater design flexibility, higher signal integrity, efficient power distribution and space savings. These factors make 4-layer PCBs suitable for a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics, telecommunications, industrial equipment and automotive systems.
Advantages of 4-Layer PCBs over Lower-Layer PCBs
1. Enhanced Design Flexibility and Complexity
One of the key benefits of 4-layer boards is the increased design flexibility and complexity they offer. With two internal signal layers and two internal power or ground plane layers, designers have more routing options and can accommodate complex circuit designs. The additional layers allow the placement of more components, intricate interconnects and optimised signal paths, enabling the realisation of advanced functionality.
2. Improved Signal Integrity and Reduced EMI
Signal integrity is critical in electronic designs and 4-layer PCBs excel in this respect. The internal power and ground planes act as solid references, providing a low impedance return path for signal traces. This helps to minimise signal distortion, noise and crosstalk. The presence of dedicated power and ground planes also helps to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources, resulting in improved overall system performance and reliability.
3. Enhanced Power Distribution and Thermal Management
4-layer PCBs offer advantages in power distribution and thermal management. The internal power and ground planes act as effective power distribution networks, providing low impedance paths for power and ground connections. This reduces voltage drops and ensures a stable power supply to components, reducing the risk of power-related problems.
In addition, the internal planes in 4-layer boards can be used as heat sinks or thermal planes, helping to dissipate heat generated by power components. This improves thermal management, prevents overheating and increases the overall reliability and lifetime of the electronic device.
4. Potential for Miniaturization and Space-saving
The additional layers in 4-layer PCB boards enable more compact designs compared to lower layer count boards. By effectively utilising the internal signal and plane layers, designers can achieve higher component density and more efficient routing, resulting in miniaturised and space-saving PCB layouts. This is particularly beneficial for devices with size constraints or where form factor optimisation is critical.
Applications
1. Telecommunications: The telecommunications industry makes extensive use of 4-layer printed circuit boards for various applications. These PCBs are used in communications equipment such as routers, switches, modems and network equipment. The high-speed transmission requirements and complex circuitry in these devices make 4-layer PCBs ideal for achieving optimum signal integrity and efficient power distribution.
2. Consumer electronics: Consumer electronics devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops and gaming consoles, often incorporate 4-layer PCBs. These PCBs enable miniaturisation and compact designs that are essential for portable and space-constrained devices. The additional layers enable complex circuitry and high-density component placement, supporting the advanced features demanded by consumers.
3. Automotive: The automotive industry relies on 4-layer PCBs for various applications. They are used in engine control units (ECUs), infotainment systems, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and other electronic modules. The robustness, reliability and miniaturisation capabilities of 4-layer PCBs are critical in the automotive environment, where space is limited and resistance to vibration, temperature variations and harsh conditions is essential.
4. Industrial control systems: Industrial control systems, including programmable logic controllers (PLCs), automation systems and robotics, often use 4-layer PCBs. These PCBs provide the necessary complexity and reliability to support the demanding requirements of industrial applications. They enable precise control, efficient power distribution and reliable communication within complex control systems.
5. Medical devices: Medical devices such as patient monitoring systems, imaging equipment and implantable devices often rely on 4-layer printed circuit boards. These PCBs enable the integration of sophisticated electronics, sensors and wireless communication modules into compact and reliable medical devices. The high-density interconnects and robust design of 4-layer PCBs contribute to the accuracy and functionality of medical devices.
These are just a few examples of the industries and products where 4-layer PCBs are widely used. Ucreate's enhanced design flexibility, improved signal integrity, efficient power distribution and miniaturisation potential make 4-layer PCBs suitable for a wide range of applications in various industries.
Related Posts:
1.The Differences and Applications of Single-Sided PCBs, Double-Sided PCBs, and Multilayer PCBs
2.Why Are Multilayer PCB Even-numbered Layers?
3.What Are The Different Types of PCBs?
Welcome to consult our sales engineer with BOM list and Gerber file