Type 1 – Single Layer
Single-sided flexible wiring containing one conductive layer and one or two polyimide outer cover layers.
-
One conductive layer, either laminated between two insulating layers or uncovered on one side.
-
Access holes to conductors can be on either one or both sides.
-
No plating in component holes.
-
Components, stiffeners, pins and connectors can be used.
-
Suitable for static and dynamic flex applications.

A Type 1 flex structure with 2 cover layers, access holes on both sides and no plating in the in the component holes.
Type 2 – Double Layer
Double-sided flexible printed wiring containing two conductive layers with plated through holes, with or without stiffeners.
-
Two conductive layers with an insulating layer between; outer layers can have covers or exposed pads.
-
Plated through-holes provide connection between layers.
-
Access holes or exposed pads without covers can be on either or both sides; vias can be covered on both sides.
-
Components, stiffeners, pins and connectors can be used.
-
Suitable for static and dynamic flex applications.


A Type 2 flex structure with access holes on both sides and plated through holes.
Type 3 – Multilayer
Multilayer flexible printed wiring containing three or more conductive layers with plated-through holes, with or without stiffeners.
-
Three or more flexible conductive layers with flexible insulating layers between each one; outer layers can have covers or exposed pads.
-
Plated through-holes provide connection between layers.
-
Access holes or exposed pads without covers can be on either or both sides.
-
Vias can be blind or buried.
-
Components, stiffeners, pins and connectors can be used.
-
Typically used for static flex applications.


A Type 3 flex structure with access holes on both sides and plated through holes.
Type 4 – Multilayer Rigid-Flex
Multilayer rigid and flexible material combinations (Rigid-Flex) containing three or more conductive layers with plated-through holes. Rigid-flex has conductors on the rigid layers, which differentiates it from multilayer circuits with stiffeners.
-
Two or more conductive layers with either flexible or rigid insulation material as insulators between each one; outer layers can have covers or exposed pads.
-
Plated through-holes extend through both rigid and flexible layers (apart from blind and buried vias).
-
Access holes or exposed pads without covers can be on either or both sides.
-
Vias or interconnects can be fully covered for maximum insulation.
-
Components, stiffeners, pins, connectors, heat sinks, and mounting brackets can be used.
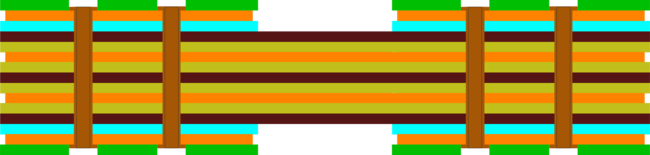
A Type 4 rigid-flex structure, the rigid sections are formed by adding rigid layers to the outside of the flex structure.